Create Sorted Array through Instructions
문제 내용
빈 Array nums[]가 있고
이곳에 입력할 값 Array 인 instructions가 있다고 할때
instructions Array의 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 nums[] Array에 값을 추가해 나간다.
단, nums[]의 Array는 정렬이 되어야 한다.
정렬을 위한 cost는 다음과 같이 정의한다.
Min( 현재 있는 nums 중 insturction[i] 보다 작은 숫자의 갯수, 현재 있는 nums 중 instruction[i]보다 큰 숫자의 갯수 )
예를 들자면 [1,2,3,4,5]의 nums가 주어졌을 때
3을 넣기 위한 최소의 cost 값은 1,2 => 2개, 4,5 => 2개 min(2,2) 임으로 cost 2가 사용된다.
이후 nums의 모습은 [1,2,3,3,4,5]가 된다.
접근 방법
가장 쉬운 방법은 instruction을 처리할 때 마다. full search를 하는 것이다.
예를 들자면 [3,4,1,7,9] 가 있고,
Instruction에서 5가 나왔다고 하면
3,4,1 => 3개
7,9 => 2개
이런식으로 처리하면 된다.
그런데 제한 값을 보면
- 1 <= instructions.length <= 10^5
임으로 full Search를 할 경우 시간 초과가 발생 할 수 없다.
O(N^2)
그래서 다음과 같이 Segment Tree를 사용하는 방법을 선택했다.
Segment Tree
특정 범위의 Array 의 Sum을 빠르게 하기 위해 만들어진 기법이다.
만약 [3,5,8,1,3,9] 라고 하는 Array가 주어 졌다고 생각해 보자.
이를 Tree로 만들면 다음과 같다.

이 Tree에서 주의해서 봐야할 점은 우측에 '0' 이다. 반듯이 Tree의 Balance를 맞춰줘야 한다.
이렇게 Tree가 만들어지면 다음과 같이 Query가 가능하다.
[3,5,8,1,3,9] 에서
- 0 ~ 5까지의 Sum은?

상기와 같이 Index 0과 5 즉
- Left Index < Right Index인 관계에서
- Left Index가 짝수이면 상위 노드로 올라간다.
- Right Index 가 홀수이면 상위 노드로 올라간다
라는 개념을 만들 수 있다.
그런데 상위 노드의 Index는 몇인가?
이를 처리하기 위해서 Root Node는 Base 1부터 하는 Array위치를 주게 된다. 다음과 같다.
[<Not use>, 29,17,12,8,9,12,0,3,5,8,1,3,9,0,0]
이 Index를 다시 그림으로 보자면 다음과 같다.

이 그림을 보면 Segment Tree의 최소 필요 Array의 양은
- Original Array Length * 2 + 1 (1 Base Array를 만들어야 함으로 1이 필요하다)
이 된다.
계속해서 Search를 해보겠다.

여기에서 우측 6번 Index는 짝수가 됨으로 12를 저장하고 Index를 하나 줄여 줌으로써 더이상 우측 Search가 일어나지 않게 한다.
마지막으로 4번과 5번 Index를 한단계 올리면 최종적으로 2번 인덱스에서 만나게 된다.
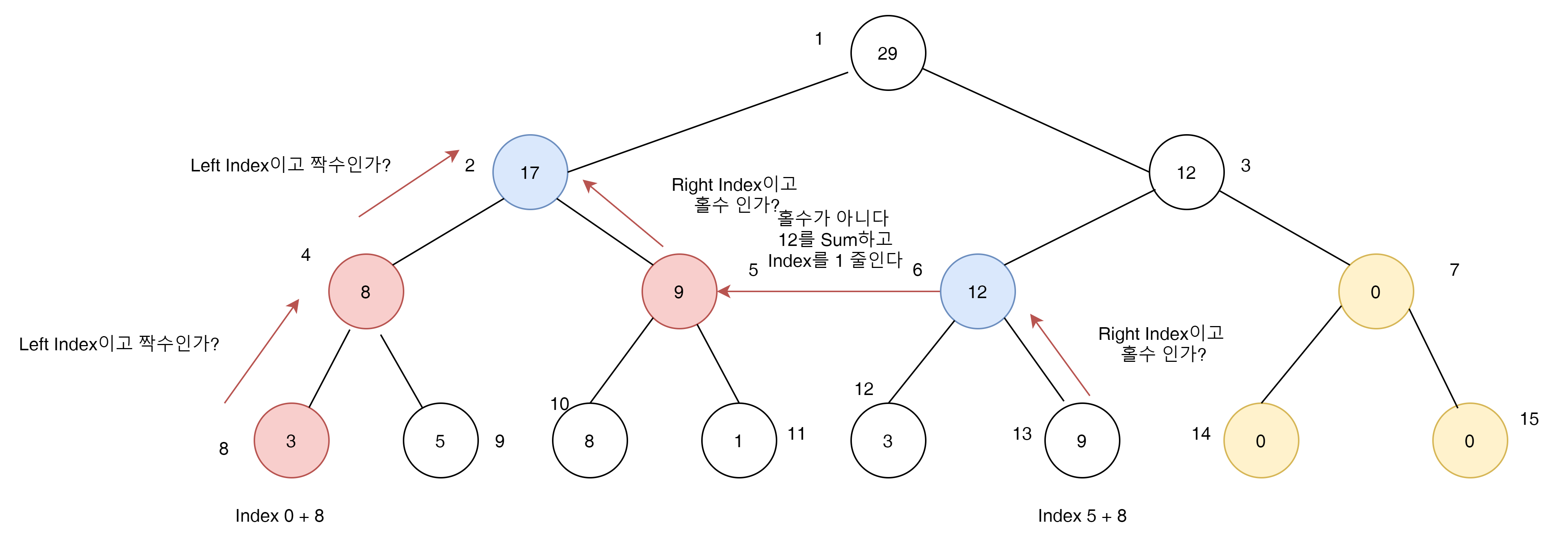
여기서 17이라는 값을 다시 Sum에 저장하고 Node Search는 여기에서 종료한다.
답은 17 + 12인 29가 된다.
Segment Tree에서 주의 해야할 것을 정리 하자면 다음과 같다.
- 입력된 값의 Index 시작점은 0이다. Segment Tree의 위치로 보면 입력된 Array 길이 + 0이다.
- 상위에 그림을 보면 8개를 입력하고, 사용자가 입력한 Index의 시작이 0이라는 것을 보면 된다.
- Right Index는 홀수를 기준으로 한다. 만약에 짝수 즉 Index 12가 들어온다면 Node를 위로 올라갈 필요 없이 3을 Sum에 저장하고 Node 차수를 하나 내려서 Index 11로 시작해야 한다.
이를 이용해서 만든 Segment Tree는 다음과 같다.
let SegmentTree = (function (){
function SegmentTree(width = 100000){
this.HOLD = width;
this.array = new Array(width * 2 + 1).fill(0);
};
SegmentTree.prototype.updateIdx = function (idx, val){
idx += this.HOLD;
this.array[idx] = val;
while(idx > 1){
idx = Math.floor(idx/2);
this.array[idx] = this.array[idx*2] + this.array[idx*2+1];
}
};
SegmentTree.prototype.query = function(left, right){
if(right == null){
right = this.HOLD;
}
let sum = 0;
let leftIdx = this.HOLD + left;
let rightIdx = this.HOLD + right;
while (leftIdx <= rightIdx) {
if(leftIdx === rightIdx){
sum += this.array[leftIdx];
break;
}
if((leftIdx & 1) === 1){
sum += this.array[leftIdx];
leftIdx += 1;
}
if((rightIdx & 1) !== 1){
sum += this.array[rightIdx];
rightIdx -= 1;
}
leftIdx >>= 1;
rightIdx >>= 1;
}
return sum;
};
return SegmentTree;
})();이 Segment Tree는 Update시 O(LogN), Query시 O(LogN)의 속도를 갖는다.
사용 방법은 아래와 같다.
let st = new SegmentTree(8);
st.updateIdx(0,3);
st.updateIdx(1,5);
st.updateIdx(2,8);
st.updateIdx(3,1);
st.updateIdx(4,3);
st.updateIdx(5,9);
let res = st.query(0, 7);
console.log(res);
이 라이브러리를 이용해서 다음과 같은 접근방법을 사용하면 본 문제를 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
들어올 수 있는 모든 숫자의 범위는
- 1 ~ 100,000
이다.
십만개의 Array를 만들고 각 Array Index별 Count를 처리한다.
예를 들자면
[1,2,3]
이면
[1,1,1]
이다. Index 0일때 1이라고 보면 1이 한개 2가 한개 3이 한개 이기 때문이다.
본 문제는 특정 숫자의 좌측에 존재하는 작은 수의 갯수,
특정 숫자의 우측에 존재하는 큰 수의 갯수를 빠르게 구하는 것이 중요하다.
[1,4,5,2,7]
인 상태에서 3을 구한다고 예를 들자면
Index count는
[1,1,0,1,1,0,1] 이 되고
3보다 작은 수의 갯수는 2 많은 수의 갯수는 3이된다.
Min(2,3) = 3
이 되는 것이다.
이를 상기 코드에 추가하면 다음과 같은 코드가 된다.
let SegmentTree = (function (){
function SegmentTree(width = 100000){
this.HOLD = width;
this.array = new Array(width * 2 + 1).fill(0);
};
SegmentTree.prototype.update = function (val){
let idx = this.HOLD + val -1;
this.array[idx]++;
while(idx > 1){
idx = Math.floor(idx/2);
this.array[idx] = this.array[idx*2] + this.array[idx*2+1];
}
};
SegmentTree.prototype.updateIdx = function (idx, val){
idx += this.HOLD;
this.array[idx] = val;
while(idx > 1){
idx = Math.floor(idx/2);
this.array[idx] = this.array[idx*2] + this.array[idx*2+1];
}
console.log(this.array);
};
SegmentTree.prototype.query = function(left, right){
if(right == null){
right = this.HOLD;
}
let sum = 0;
let leftIdx = this.HOLD + left;
let rightIdx = this.HOLD + right;
while (leftIdx <= rightIdx) {
if(leftIdx === rightIdx){
sum += this.array[leftIdx];
break;
}
if((leftIdx & 1) === 1){
sum += this.array[leftIdx];
leftIdx += 1;
}
if((rightIdx & 1) !== 1){
sum += this.array[rightIdx];
rightIdx -= 1;
}
leftIdx >>= 1;
rightIdx >>= 1;
}
return sum;
};
return SegmentTree;
})();Update 함수를 추가 하였다.
여기서 신경 써야할 코드는 다음과 같다.
let idx = this.HOLD + val -1;1이 Zero Base여야 함으로 val이 1일때 Index를 하나 줄여서 zero Index가 1의 카운터 갯수로 볼수 있게 해주는 것이다.
var createSortedArray = function(instructions) {
let segment = new SegmentTree();
let cost = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < instructions.length; i++) {
cost += Math.min(segment.query(0, instructions[i]-2), segment.query(instructions[i]));
segment.update(instructions[i]);
}
return cost % 1000000007;
};최종적으로 이렇게 코드를 짜면 되는데 설명을 하자면 다음과 같다.
cost += Math.min(segment.query(0, instructions[i]-2), segment.query(instructions[i]));특정 숫자 instructions[i]를 기준 점으로 왼쪽의 count sum과 오른쪽 count sum을 비교하는 것이다.
여기서 -2를 한이유는 Zerobase를 맞춰주기 위해서 -1을 하였고, 현재 자기 자신은 빼야함으로 -1을 더해서 -2를 했다.
예를 들자면
[0,0,0]
이라고 하는 Index count가 들어왔고
3이 기준 Index라고 하면 Query는 0~1(integer로는 1~2)Index를 Search 해야함으로
0부터 -2를 뺀 1까지의 범위를 Query한 것이다.
오른쪽은 3이 기준일경우 Index위치는 2임으로
Instructions[i]를 그대로 넣게 되면 Index위치의 오른쪽 +1인 3부터 Query하게 된다.
segment.update(instructions[i]);cost 계산을 완료하고 해당 값을 Insert 해준다.
return cost % 1000000007;최종적으로 모듈러를 나눠준다.
최종 코드는
let SegmentTree = (function (){
function SegmentTree(width = 100000){
this.HOLD = width;
this.array = new Array(width * 2 + 1).fill(0);
};
SegmentTree.prototype.update = function (val){
let idx = this.HOLD + val -1;
this.array[idx]++;
while(idx > 1){
idx = Math.floor(idx/2);
this.array[idx] = this.array[idx*2] + this.array[idx*2+1];
}
};
SegmentTree.prototype.updateIdx = function (idx, val){
idx += this.HOLD;
this.array[idx] = val;
while(idx > 1){
idx = Math.floor(idx/2);
this.array[idx] = this.array[idx*2] + this.array[idx*2+1];
}
console.log(this.array);
};
SegmentTree.prototype.query = function(left, right){
if(right == null){
right = this.HOLD;
}
let sum = 0;
let leftIdx = this.HOLD + left;
let rightIdx = this.HOLD + right;
while (leftIdx <= rightIdx) {
if(leftIdx === rightIdx){
sum += this.array[leftIdx];
break;
}
if((leftIdx & 1) === 1){
sum += this.array[leftIdx];
leftIdx += 1;
}
if((rightIdx & 1) !== 1){
sum += this.array[rightIdx];
rightIdx -= 1;
}
leftIdx >>= 1;
rightIdx >>= 1;
}
return sum;
};
return SegmentTree;
})();
var createSortedArray = function(instructions) {
let segment = new SegmentTree();
let cost = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < instructions.length; i++) {
cost += Math.min(segment.query(0, instructions[i]-2), segment.query(instructions[i]));
segment.update(instructions[i]);
}
return cost % 1000000007;
};이 된다.
최종 Timecomplexity는 O(NumberOfInstructions Log(Max Value))가 된다.
'Problem Solving' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2진수 최 우측 1의 자리 찾아내기 (0) | 2021.05.02 |
|---|---|
| Segment Tree (0) | 2021.05.02 |
| Employee Free Time (0) | 2021.05.01 |
| First Missing Positive (0) | 2021.05.01 |
| Merge k Sorted Lists (0) | 2021.04.29 |
